In a current examine printed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers analyzed the mortality developments amongst adults of working age in addition to retirement age (above 65 years) in america (US) and their relative affect on life expectancy stagnation noticed post-2010. They discovered that elevated mortality within the retirement age group, in addition to the years of life misplaced (YLL) and extra deaths in 2019, had a extra vital affect on life expectancy stagnation than the elevated mortality within the working-age inhabitants.
The life expectancy development within the US has stalled since 2010 regardless of the advances made in science and healthcare. Earlier research attributed this stagnation to the elevated mortality in middle-aged and youthful adults, prompted primarily by drug overdose, cardiometabolic illnesses, and suicide. The current examine aimed to research, for the primary time, the relative contributions to mortality amongst adults of working age and retirement age within the US.
 Transient Report: The “double jeopardy” of midlife and previous age mortality developments in america. Picture Credit score: Hyejin Kang / Shutterstock
Transient Report: The “double jeopardy” of midlife and previous age mortality developments in america. Picture Credit score: Hyejin Kang / Shutterstock
In regards to the examine
This examine used statistical analyses to research the affect of mortality developments amongst working-age and older-age adults on life expectancy stagnation within the US. The time period “double jeopardy” is coined to depict the mortality developments in these two age teams.
Annual mortality charges have been obtained from the Human Mortality Database. The researchers calculated counterfactual dying charges between 2000 and 2019 by extrapolating the typical change in all-cause mortality particular to intercourse and single-year-age-group from 2000–2009 to 2010–2019. They utilized these charges to 4 age teams: above 25 years, 25–49 years, 50–64 years, and above 65 years. Moreover, the surplus deaths and YLL have been calculated and summed at annually of age between 5-year age teams.
To comprehensively assess age-specific contributions in conditions that in a different way weight the age teams, the examine used three inhabitants indicators of mortality: life expectancy, YLL, and extra deaths. The unbiased results of mortality charges in working-age and retirement-age adults have been mapped to those indicators between 2010 and 2019 and in comparison with the interval 2000 to 2009, when the life expectancy at 25 years of age (e25) elevated for men and women by 1.36 years and 1.72 years, respectively.
Outcomes and dialogue
As per the findings, e25 elevated by 0.41 and 0.17 years for men and women, respectively. Had the pattern for mortality in age above 25 years between 2000 and 2009 continued till 2019, e25 would have elevated for each males (by 2.1 years) and ladies (by 1.2 years).
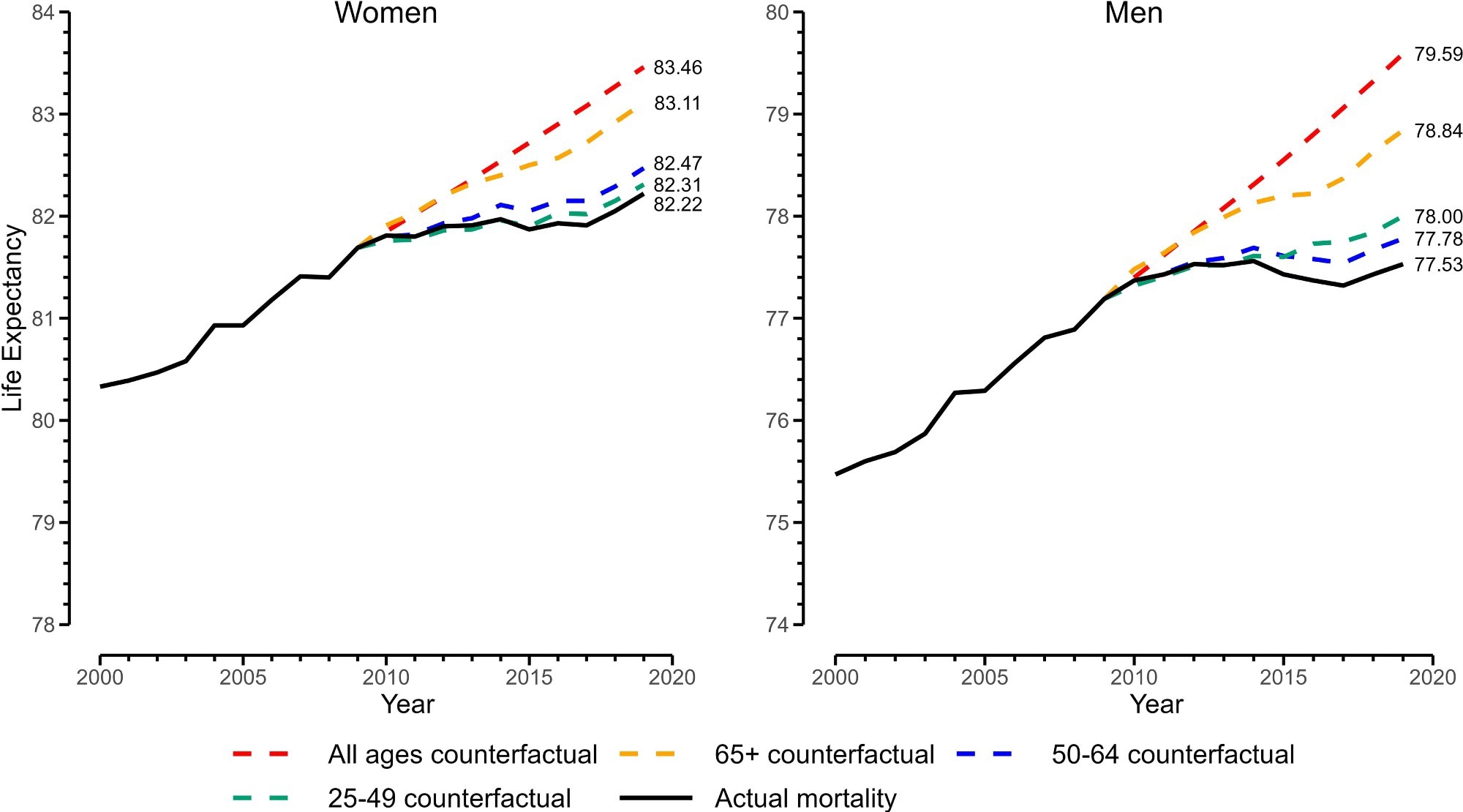 Actual and counterfactual life expectations at age 25, 2000 to 2019. Observe: y axis is life expectancy at delivery calculated from including 25 y to e25 (life expectancy at age 25, conditional on surviving to age 25 y).
Actual and counterfactual life expectations at age 25, 2000 to 2019. Observe: y axis is life expectancy at delivery calculated from including 25 y to e25 (life expectancy at age 25, conditional on surviving to age 25 y).
To isolate the impact of previous age, solely the mortality fee of age above 65 years was allowed to proceed at its 2000–2009 tempo till 2019, whereas the working-age developments remained at their precise ranges. Nevertheless, as an alternative of retirement age mortality, if the working-age mortality (ages 25–49 years and 50–64 years) have been allowed to proceed on the 2000–2009 tempo till 2019, the e25 would solely have elevated barely. These findings thus counsel that though the e25 stagnation is affected by mortality developments on the working age in addition to the retirement age, the latter developments have a extra vital affect. Moreover, it was noticed that the impact for ages above 65 years was contributed to extra by opposed developments within the age group 65–84 than by the age group above 85.
Within the extra dying evaluation, the affect of actual and counterfactual dying charges was in contrast on the 2019 inhabitants. As per the examine, 76% of the 230,000 extra deaths in males and 81% of the 157,000 extra deaths in ladies occurred at ages above 65 years. Extra evaluation reveals that the mortality in ages above 65 years accounts for YLL in each ladies (61%) and males (55%). As per the examine, the coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic additional compounded the impact on preexisting life expectancy stagnation post-2019.
The authors mentioned numerous interconnected components contributing to those mortality developments, similar to financial inequality, social isolation, and insufficient healthcare entry. The counterfactual dying charges introduced on this examine have been akin to these present in Japan, Switzerland, the UK, and Italy. Additional analysis is required to raised perceive the causes of mortality and the contribution of upstream components to this “double jeopardy.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, the findings counsel a higher affect of mortality developments of retirement-age people on life expectancy stagnation within the US. The examine highlights the pressing want to deal with the “double jeopardy” of midlife and previous age mortality within the US, which can have vital implications for inhabitants well being and well-being. Complete and coordinated coverage interventions geared toward addressing the underlying causes and determinants of those mortality developments could possibly be useful for enhancing well being outcomes within the US inhabitants.


